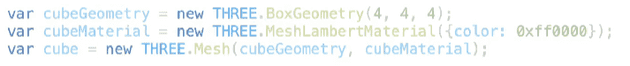Renderer, Scene, Camera
- Renderer
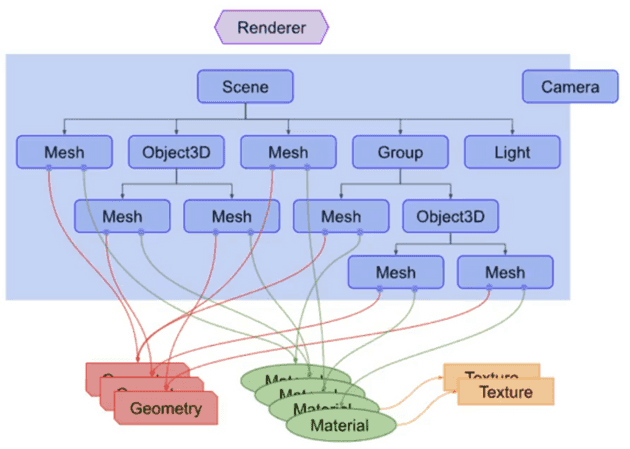
- three.js의 주요 오브젝트
- Scene과Camera를 Renderer로 넘기고 이것은 카메라의 frustum 내부에 포함되는3d scene의 일부분을 캔버스에 렌더링한다.
-
Scene
- 렌더링할 모든 오브젝트를 저장하고 보존하는 데 사용되는 컨테이너
-
Scene Graph
- Scene에 존재하는 오브젝트를 계층구조로 표현한 그래프.
-
Camera
- 다른 오브젝트와 달리 Scene graph에 포함되어있지 않아도 된다.
- 다른 오브젝트의 자식으로서 존재할 수도 있다.
- 카메라는 여러 개가 있을 수 있다.
-
Others
Adding Scene, Camera, Renderer
WebGL에서는 shader에서 모두 직접 구현했어야 했다.
⇒Three.js에서는 게임엔진처럼 기본적인 기능을 제공해주고 있다.
-
Scene 생성
scene = new THREE.Scene() -
Camera 생성
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000 ) // position and point the camera to the center of the scene camera.position.x = 20 camera.position.y = 0 camera.position.z = 0 camera.lookAt(scene.position) -
Renderer 생성
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer() renderer.setClearColorHex() renderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xeeeeee)) renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight) -
Axes, Object 생성
축을 생성하고 원통과 원뿔형 객체를 obj1이라는 오브젝트에 추가하여 화살표 모양의 오브젝트를 생성한다.
// show axes in the screen, X: red, Y: green, Z: blue var axes = new THREE.AxisHelper(20) scene.add(axes) // create an object var axes2 = new THREE.AxisHelper(5) var cylinderGeometry = new THREE.CylinderGeometry(0.5, 0.5, 3, 12) var cylinderMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({ wireframe: false, }) var cylinder = new THREE.Mesh(cylinderGeometry, cylinderMaterial) const geometry = new THREE.CylinderGeometry(0, 0.7, 2, 12) const material = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({ wireframe: false }) const cone = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material) var axes2 = new THREE.AxisHelper(2) var obj1 = axes2.clone() cone.position.y = 2.5 cylinder.add(cone) cylinder.position.y = 1.5 obj1.add(cylinder) -
Object 복제
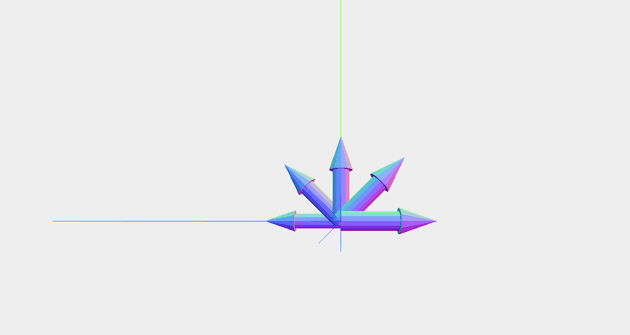
앞서 만든 화살표 모양의 객체를 복제한 4개의 객체를 생성한 뒤 위치를 설정해준다.
// make 4 clones of the object var obj2 = obj1.clone() var obj3 = obj1.clone() var obj4 = obj1.clone() var obj5 = obj1.clone() // and place them along x aixs obj1.position.x = 1 obj2.position.x = 2 obj3.position.x = 3 obj4.position.x = 4 obj5.position.x = 5복제한 각 객체가 가리키는 방향이 방사형으로 보이게 하기 위해 0~180도에 대해 선형 보간을 해준다.
function interpolateAngle(S, E, C, A1, A2) { // S: start value // E: end value // C: current value // A1: start angle // A2: end angle return (A1 * (5 - C) + A2 * (C - 1)) / 4 }var startAngle = Math.PI / 2 var endAngle = -Math.PI / 2 obj1.rotation.x = startAngle obj5.rotation.x = endAngle obj2.rotation.x = interpolateAngle( obj1.position.x, obj5.position.x, obj2.position.x, obj1.rotation.x, obj5.rotation.x ) obj3.rotation.x = interpolateAngle( obj1.position.x, obj5.position.x, obj3.position.x, obj1.rotation.x, obj5.rotation.x ) obj4.rotation.x = interpolateAngle( obj1.position.x, obj5.position.x, obj4.position.x, obj1.rotation.x, obj5.rotation.x )씬에 각 객체들을 추가한다.
scene.add(obj1) scene.add(obj2) scene.add(obj3) scene.add(obj4) scene.add(obj5) -
Renderer의 Output을 html 요소에 추가
이로써 렌더링한 결과물을 웹 페이지 상에 띄울 수 있다.
// add the output of the renderer to the html element document.getElementById("WebGL-output").appendChild(renderer.domElement) -
렌더링
완성된 씬과 카메라를 렌더링한다.
// render the scene renderer.render(scene, camera)
전체 코드
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>assignment01</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../libs/three.js"></script>
<style>
body {
/* set margin to 0 and overflow to hidden, to
use the complete page */
margin: 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Div which will hold the Output -->
<div id="WebGL-output"></div>
<!-- Javascript code that runs our Three.js examples -->
<script type="text/javascript">
// once everything is loaded, we run our Three.js stuff.
function init() {
// create a scene, that will hold all our elements such as objects, cameras and lights.
var scene = new THREE.Scene()
// create a camera, which defines where we're looking at.
var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
75,
window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,
0.1,
1000
)
// create a render and set the size
var renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer()
renderer.setClearColorHex()
renderer.setClearColor(new THREE.Color(0xeeeeee))
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
// show axes in the screen, X: red, Y: green, Z: blue
var axes = new THREE.AxisHelper(20)
scene.add(axes)
// create an object
var axes2 = new THREE.AxisHelper(5)
var cylinderGeometry = new THREE.CylinderGeometry(0.5, 0.5, 3, 12)
var cylinderMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({
wireframe: false,
})
var cylinder = new THREE.Mesh(cylinderGeometry, cylinderMaterial)
const geometry = new THREE.CylinderGeometry(0, 0.7, 2, 12)
const material = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({ wireframe: false })
const cone = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material)
var axes2 = new THREE.AxisHelper(2)
var obj1 = axes2.clone()
cone.position.y = 2.5
cylinder.add(cone)
cylinder.position.y = 1.5
obj1.add(cylinder)
// make 4 clones of the object
var obj2 = obj1.clone()
var obj3 = obj1.clone()
var obj4 = obj1.clone()
var obj5 = obj1.clone()
// and place them along x aixs
obj1.position.x = 1
obj2.position.x = 2
obj3.position.x = 3
obj4.position.x = 4
obj5.position.x = 5
var startAngle = Math.PI / 2
var endAngle = -Math.PI / 2
obj1.rotation.x = startAngle
obj5.rotation.x = endAngle
obj2.rotation.x = interpolateAngle(
obj1.position.x,
obj5.position.x,
obj2.position.x,
obj1.rotation.x,
obj5.rotation.x
)
obj3.rotation.x = interpolateAngle(
obj1.position.x,
obj5.position.x,
obj3.position.x,
obj1.rotation.x,
obj5.rotation.x
)
obj4.rotation.x = interpolateAngle(
obj1.position.x,
obj5.position.x,
obj4.position.x,
obj1.rotation.x,
obj5.rotation.x
)
scene.add(obj1)
scene.add(obj2)
scene.add(obj3)
scene.add(obj4)
scene.add(obj5)
// position and point the camera to the center of the scene
camera.position.x = 20
camera.position.y = 0
camera.position.z = 0
camera.lookAt(scene.position)
// add the output of the renderer to the html element
document.getElementById('WebGL-output').appendChild(renderer.domElement)
// render the scene
renderer.render(scene, camera)
}
function interpolateAngle(S, E, C, A1, A2) {
// S: start value
// E: end value
// C: current value
// A1: start angle
// A2: end angle
return (A1 * (5 - C) + A2 * (C - 1)) / 4
}
window.onload = init
</script>
</body>
</html>